class ii elastics effect
Class 2 elastics effect During this period Class II elastics are used for various periods of time. A systematic review done by Janson et al.

Orthodontics In Spanish Fort Bay Minette Foley Orthodontics Fairhope Strickland Orthodontics
Are Class II elastics7 In spite of their popularity8 some authors have attributed several side effects to the use of Class II elasticseg loss of mandibular anchorage proclination of mandibular incisors extrusion of maxil-lary incisors and even worsened smile esthetics because of increased gum exposurethus suggesting minimal.
. As the present case shows when Class II elastics are. Maximum strain on the PDL and maximum stress on alveolar. 3 Among these mandibular retrusion is the most common.
To evaluate the skeletal dentoalveolar and soft tissue effects of skeletally anchored Class II elastics and compare them with a. Class II elastics are auxiliary forces that can be classified as active elements in a fixed appliance system1 They have been used in the correction of Class II malocclusion since the early days of orthodontic treatment26 although some undesirable effects can occur depending on their vertical force vectors4610 The vertical force can extrude the mandibular molars and. A clinical outline of temporomandib- ular joint diagnosis and treatment.
Per-element distribution of linear elastic stress-strain and total displacement were computed. Below are the side effects of Class II elastics. To evaluate the effects of Class II maxillomandibular elastics on Invisalign aligners Align Technology San Jose CA USA and assess whether the type of fitting or immersion in a medium simulating the oral environment influence possible.
Labial tipping of the mandibular incisors and mesialization and extrusion of the mandibular molars. Steepening of the occlusal plane. Effect on Class II Malocclusion.
Effect of class II elastics on the moving pattern of anterior teeth. The purpose of this study was to attempt to limit the adverse effects of class II elastics by the use of mini implants placed in the mandibular arch in adolescent class II female patients. Excessive proclination of lower incisors and other undesirable consequences usually result from the use of class II elastics during orthodontic treatment.
This temporary delay in achieving its original configuration is termed as elastic. Finite Element Models that simulate the effects of Class II elastics on the mandibular arch in six different scenarios using various immobilization methods of the posterior dentition were studied. Both Class II elastics and Class II springs cause proclination of the lower incisors.
Class II elastics are effective in correcting Class II malocclusions and their effects are mainly dentoalveolar including lingual tipping retrusion and extrusion of the maxillary incisors. Lateral cephalograms were taken at the start of the experiment and again at the end 23 days later. In conclusion this study dem- onstrates that edgewise straight wire orthodontic treat- ment involving extractions and Class II elastics have no effect or little effect ie mild pain lateral to TMJ capsule on TMJ signs and symptoms.
Distal movement of the upper teeth and mesial movement of the lower teeth. Class II elastics also make use of the normal mandibular excess by allowing the usual mandibular excess to take place without maxillary mesial dentoalveolar compensation plus a mm or so of actual distal upper buccal segment movement if it is a nonextraction treatment. Full-time Class II elastic forces were applied to eight rats in order to evaluate their effects on the growth of the snout and the mandible.
But sometimes some materials take some time to return to its original configuration. 4619 Class II elastics do require some patient compliance but they tend to be more patient-friendly and tolerable and are less expensive than bite-jumping devices. The class II elastics have different effects6.
Looking at the effect of Class 2 elastics in correcting class II malocclusions concluded that Class II elastics are effective in correcting Class II malocclusions and that their. Effects upon the mandibular arch. Anthony Mair has warned about the use of Class II elasitcs with lower aligners which cause bodily root movement root prominence and gingival recession of the lower incisors.
Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. Xbow causes a temporary over-proclination of the lower incisors followed by partial. Multiple studies have reported a lack of strong evidence that the use of Class II elastics results primarily in negative side effects as was previously suggested.
Labial tipping and intrusion of the mandibular incisors. Class II malocclusion is one of the most common orthodontic conditionsaffecting approximately 30 of the population. When a elastic body is stretched and applied deforming force is removed then the body is expected to return to its original configuration instantaneously.
PDF Objective. Class 2 elastics are used from the lower first molar to the upper canine tooth Based on the scientific evidences. Effect on Class II Malocclusion.
Lower first molar extrusion. 4 There are many kinds of removable and fixed functional. Effects upon the maxillary archupper incisors are more vertical extrusion and downward movement of anterior occlusal plane backward movement of the upper arch dental distalization.
Based on the current literature we can state that Class II elastics are effective in correcting Class II malocclusions and their effects are primarily dentoalveolar. Buccal tipping of lower incisors forward movement of the entire mandibular arch. Farrar WB McCarty WL.
Eight animals served as controls. In the conventional group the results showed that class II elastics were effective in correcting class II malocclusions and their effects were mainly dentoalveolar including lingual tipping retrusion and extrusion of the maxillary incisors. 12 Skeletal Class II malocclusion can be caused by maxillary protrusion mandibular retrusion or a combination of both.
Effects of Class II maxillomandibular elastics on Invisalign aligners. An in vitro study Objective. And mesialization and extrusion of the mandibular molars.
The purpose of this investigation was to.
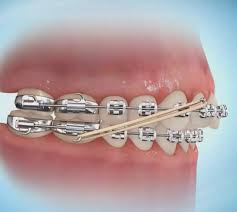
Before After Gallery Post And Pre Treatment Results
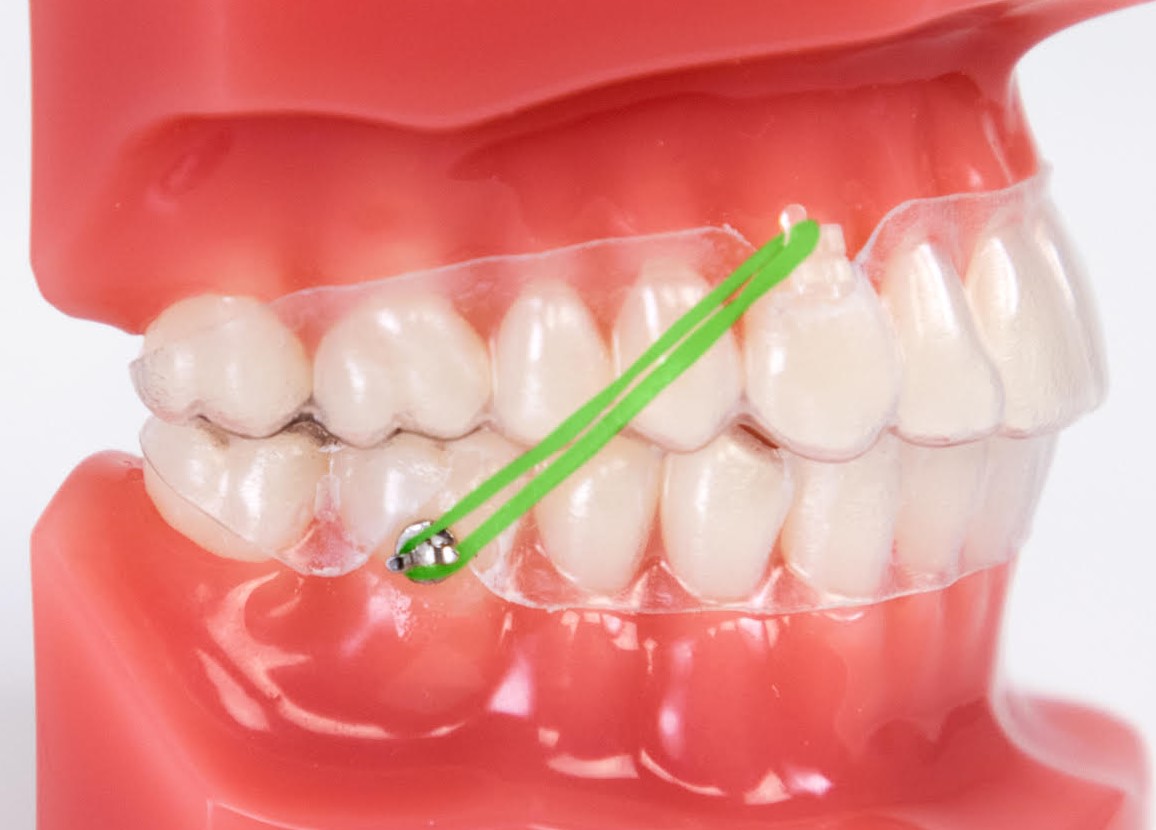
Arch Correction Simulation Acs Clearcorrect Support

Elastics Class Ii Orthodontic Treatment Youtube

Intraoral View Of Miniplate Anchored Class Ii Elastics Download Scientific Diagram
Treatment Of Class Ii Division 1 Malocclusion With Class Ii Elastics
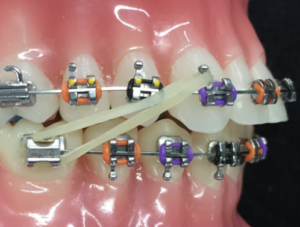
Are Class Ii Elastics As Effective As A Functional Appliance A Trial That May Answer This Question Kevin O Brien S Orthodontic Blog

Long And Short Class Ii Elastics Youtube
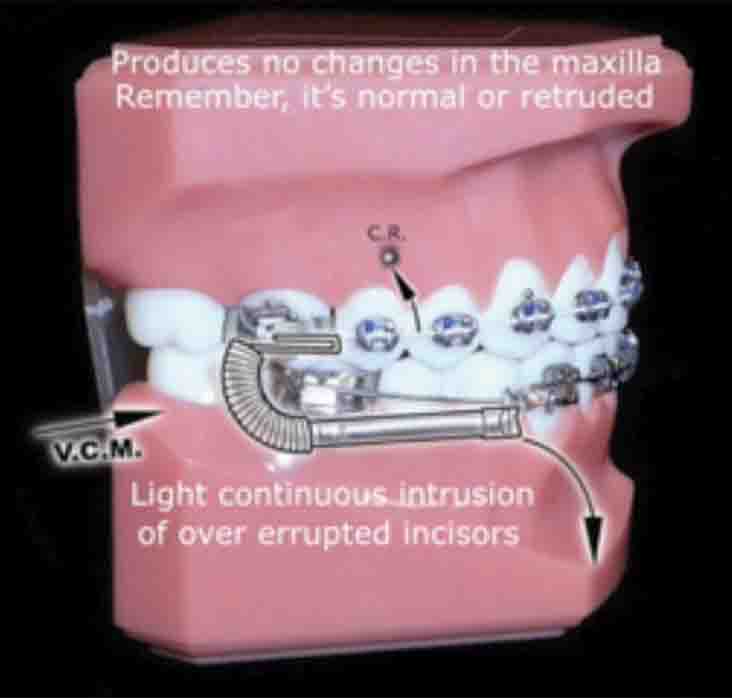
The Physics Of Class Ii Correction Orthodontic Practice Us
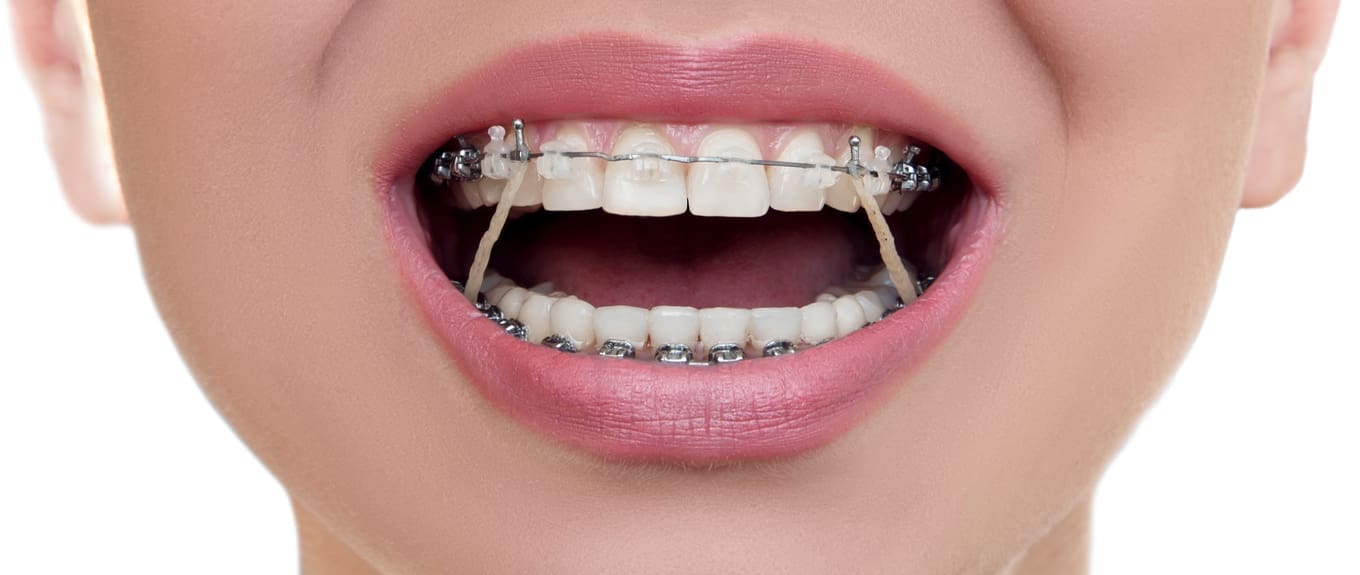
Are Class Ii Elastics As Effective As A Functional Appliance A Trial That May Answer This Question Kevin O Brien S Orthodontic Blog

Figure 2 From The Effect Of Intermaxillary Elastics In Orthodontic Therapy Semantic Scholar
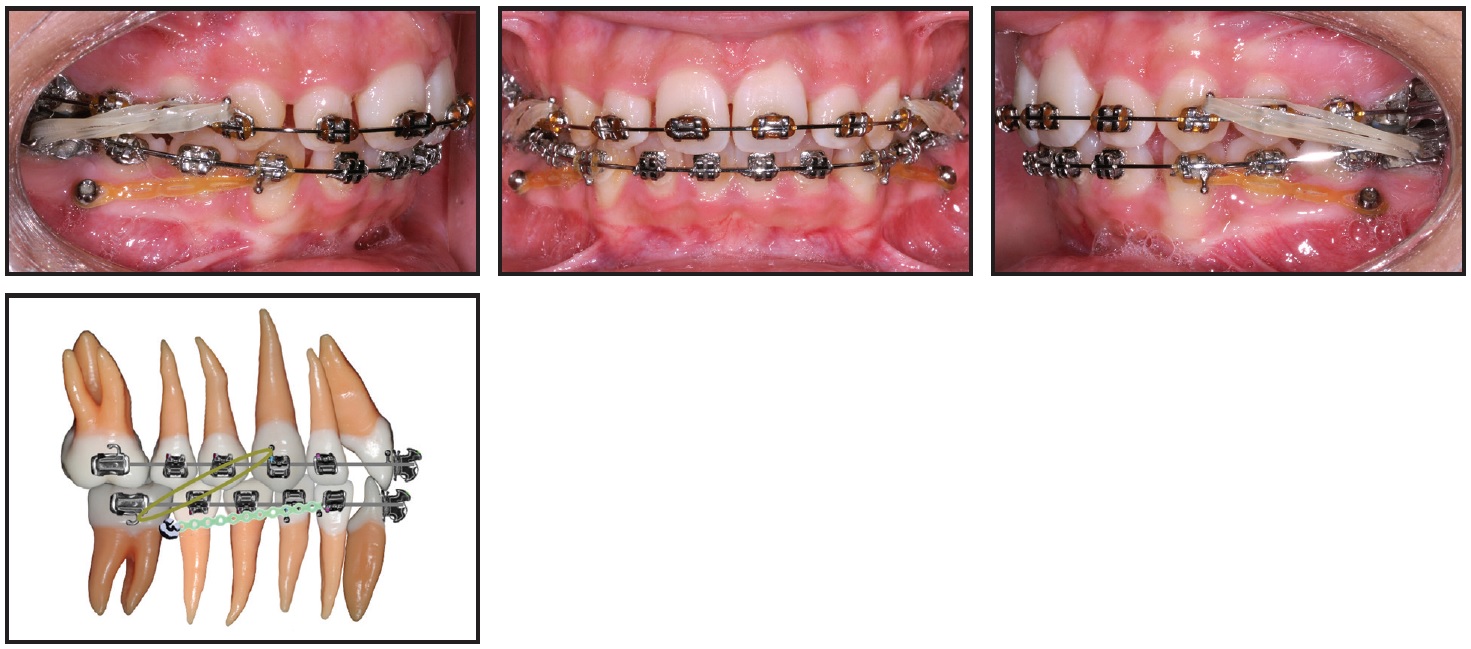
Case Report Jco Online Journal Of Clinical Orthodontics

Class Ii Elastics Lateral View Hd Edition Youtube
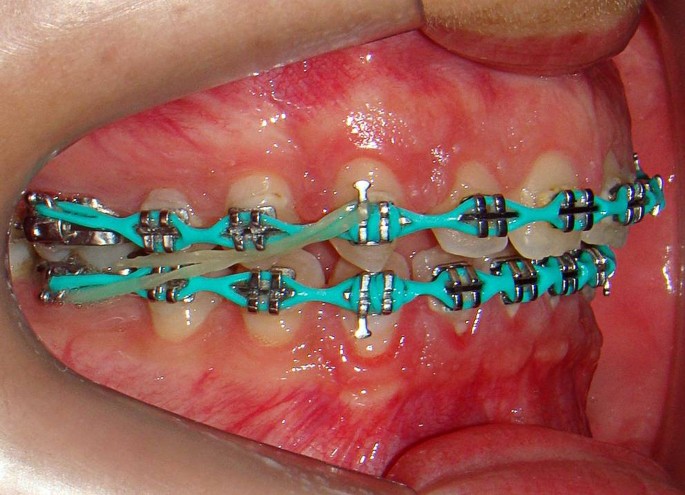
Soft Tissue Profile Changes In Angle Class Ii Patients Treated With Twin Force Or Intermaxillary Elastics A Comparison Springerlink

Direction Of Force For Class Ii Correction A Class Ii Elastics With Download Scientific Diagram

Mid Treatment Intraoral Photographs With Class Ii Elastics Download Scientific Diagram
